Many people are familiar with making a resolution to lose weight only to feel disheartened or embarrassed when their efforts fail. I deeply respect those who stay motivated and persist despite the setbacks they face.
It's understandable why some might give up entirely on this journey.

We all recognize that proper nutrition and regular exercise are fundamental to weight loss. Yet, it's important to be aware of the hidden hormonal factors that can sabotage our efforts.
These hormones can secretly induce overeating, making the weight loss journey even more challenging.
Hormonal Changes Can Trigger Overeating
Over the last year, I have touched on the hormonal subject quite a bit, yet many of you still reach out with specific questions, some just with links that have dug through the Google caves spelunking. I found a pattern in what showed up in my inbox, and it seems that the most recurrent was "hunger triggers." Let's talk about that!

Youthful Slim
Tired of the endless fluctuations in body composition? Our all-natural formula is designed to support your journey towards achieving a healthy body composition by helping you feel satisfied, controlling cravings, and maintaining balanced energy levels.
Hormones play a significant role in regulating our appetite and feelings of fullness. For women, hormonal imbalances during perimenopause, menopause, and post-menopause can greatly impact eating patterns.

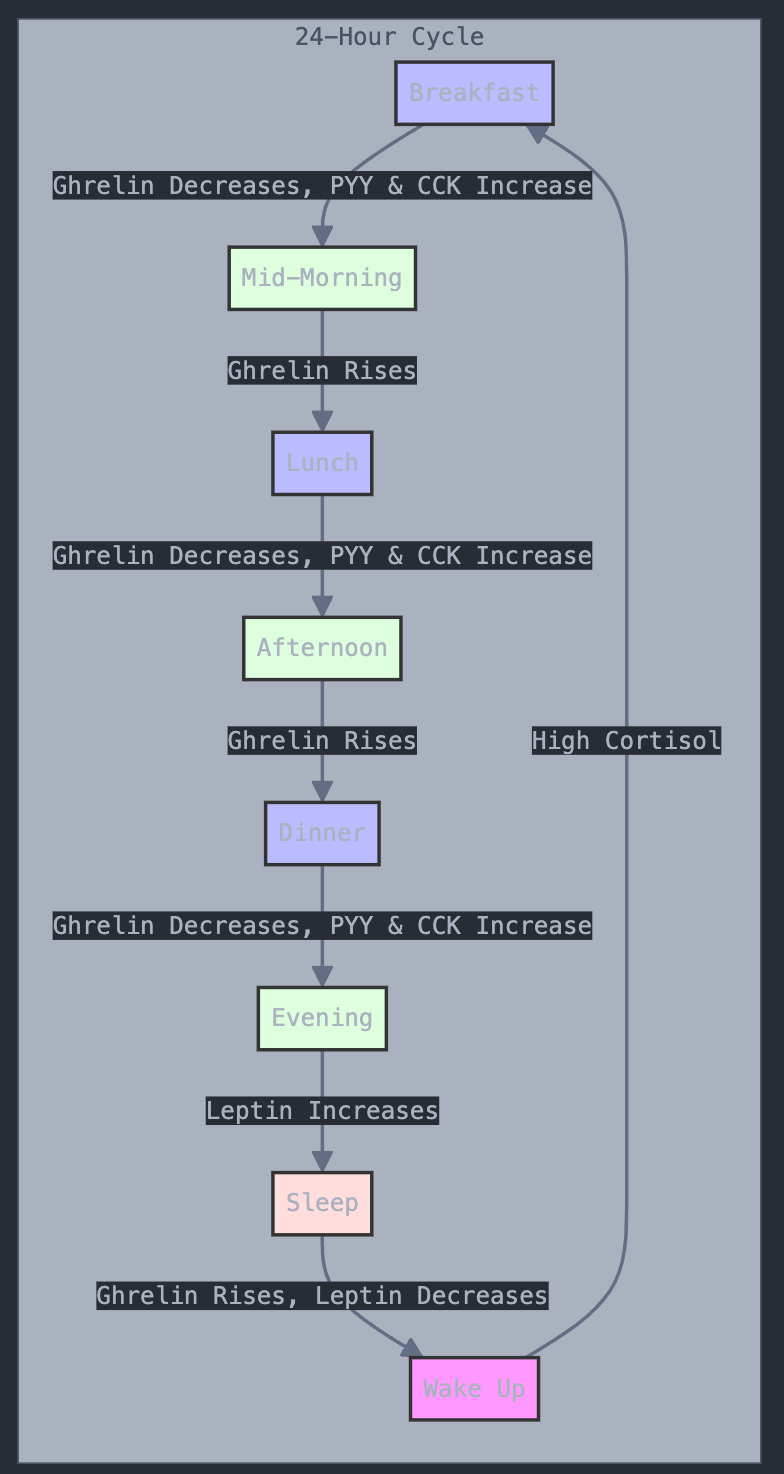
Messages sent by hormones are crucial for controlling hunger and satiety. These signals often involve the brain's hypothalamus, blood sugar levels, and various gut hormones. When changes occur in these systems, it can lead to overeating and weight gain, particularly around the belly.
The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that sits above the pituitary gland. It's responsible for many important functions, including controlling body temperature, thirst, and hunger. It also plays a role in sleep, emotions, and memory.
You don't have to become a chemistry expert, but this quick list can make you a pretty solid chemistry assistant. This list is basically the building block of a lot of joy and pain for us women on the quest to lose weight and keep our moods in check.
| Hormone | Primary Function | Produced By | Effect on Appetite | Effect on Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leptin | Signals fullness | Fat cells | Decreases | Helps maintain long-term energy balance |
| Ghrelin | Stimulates hunger | Stomach | Increases | Can lead to increased calorie intake |
| Cortisol | Stress response | Adrenal glands | Increases, especially for high-calorie foods | Can promote weight gain, particularly abdominal fat |
| Estrogen | Regulates metabolism and fat distribution | Ovaries (women), testes (men) | Varies with levels | Affects fat distribution; low levels can contribute to weight gain |
| Peptide YY (PYY) | Promotes satiety | Intestines | Decreases | Helps prevent overeating |
| Cholecystokinin (CCK) | Stimulates digestion and promotes fullness | Small intestine | Decreases | Helps control meal size |
| GLP-1 | Enhances insulin secretion and promotes satiety | Intestines | Decreases | Can lead to reduced food intake |
Key Hormones Involved
- The Hormonal Orchestra: Understanding the Key Players in Appetite and Weight Regulation
Our bodies are complex systems, and when it comes to appetite and weight regulation, hormones play a crucial role. These chemical messengers work together in a delicate balance, influencing our hunger, satiety, and metabolism. Let's dive deeper into the key hormones involved in this intricate dance:
Leptin: The Satiety Signaler
Leptin, often called the "satiety hormone," is primarily produced by fat cells. Its main job is to communicate with the brain about the body's energy stores.
- Function: Signals fullness to the brain, suppressing appetite
- Production: Mainly by adipose (fat) tissue
- Impact on weight: Helps maintain long-term energy balance
- Interesting fact: Leptin levels are proportional to body fat percentage
However, in some cases, particularly in obesity, individuals may develop leptin resistance. This means that despite having high levels of leptin, the brain doesn't respond appropriately to its signals, leading to persistent hunger and overeating.

Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone
Ghrelin is often referred to as the "hunger hormone" due to its role in stimulating appetite.
- Function: Increases appetite and food intake
- Production: Primarily in the stomach
- Impact on weight: Can lead to increased calorie consumption if levels are consistently high
- Interesting fact: Ghrelin levels typically rise before meals and fall after eating
Cortisol: The Stress Responder
Cortisol, known as the "stress hormone," can have significant effects on appetite and weight.
- Function: Helps body respond to stress; can increase appetite, especially for high-calorie foods
- Production: Adrenal glands
- Impact on weight: Chronic high levels can lead to weight gain, particularly abdominal fat
- Interesting fact: Cortisol follows a diurnal rhythm, with levels typically highest in the morning

Ultimate Cell Energy
Ultimate Cell Energy contains a powerful blend of nutrients and antioxidants to support your brain's energy production and protect against harmful free radicals.
Estrogen: The Multitasker
Estrogen, primarily known as a sex hormone, also plays a role in appetite and weight regulation.
- Function: Influences fat distribution and helps regulate food intake
- Production: Ovaries in women; small amounts in men from testosterone conversion
- Impact on weight: Fluctuations can affect appetite and weight, particularly in women
- Interesting fact: Estrogen levels drop during menopause, which can contribute to weight gain
Peptide YY (PYY) and Cholecystokinin (CCK): The Gut Messengers
These hormones are produced in the digestive system and play crucial roles in signaling fullness.
Peptide YY (PYY)
- Function: Reduces appetite and food intake
- Production: Intestines
- Impact on weight: Helps prevent overeating by promoting satiety
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
- Function: Stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and reduces appetite
- Production: Small intestine
- Impact on weight: Helps control meal size by promoting feelings of fullness
Check out the podcast!
GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1): The Dual-Action Player
GLP-1 is a hormone that has gained attention for its multiple roles in metabolism.
- Function: Enhances insulin secretion, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety
- Production: Intestines
- Impact on weight: Helps regulate blood sugar and can lead to reduced food intake
- Interesting fact: GLP-1 receptor agonists are used as medications for type 2 diabetes and weight loss
Understanding these hormones and their interactions can provide valuable insights into the complex mechanisms behind appetite and weight regulation. By recognizing the roles these chemical messengers play, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities in maintaining a healthy weight.
Chronic stress and hormonal imbalances further compound these issues. High cortisol levels from stress can prompt increased hunger and fat storage. Hormonal changes in menopause often disrupt the normal functioning of leptin and ghrelin, leading to increased appetite and potential weight gain.
Maintaining hormonal balance involves a combination of diet, exercise, stress management, and sometimes medical intervention. Understanding the complex interactions between hormones and eating behaviors helps in managing and mitigating overeating triggered by hormonal changes. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can aid in keeping these hormones in check, promoting better overall health.
In Conclusion
I hope that this different take on the building blocks has been useful to you and has quench that thirst that some of you seem to have to play little cell chemist 👩🔬 😅
I hope you enjoyed the article and the value I am trying to provide - if you have special requests or want to say HI, you know how to find me 🙋, till then stay Vibrant! 💕 💪🏼 🪞✨
References
- 9 Hormones That Affect Weight — and How to Improve Them - Healthline: This article provides insights into the various hormones, including insulin, that impact weight and how to keep them balanced.
- 7 Hormonal Imbalances That Can Hinder Weight Loss - Wellness Waterfall: It discusses the role of hormonal imbalances, including insulin resistance, in hindering weight loss efforts.
- Stopping Hormonal Triggers That Hinder Weight Loss - Doctor Emi: A detailed account on how insulin resistance manifests and its implications on weight gain and blood sugar control.
- Hormonal Misfiring: Why You’re Not Losing Weight - goop: The article covers the impacts of insulin resistance on weight gain and the body’s metabolism.
- Habit to Break Insulin Resistance - EatingWell: Provides practical advice for managing and potentially reversing insulin resistance through lifestyle changes.